Based on the theory and methods of remote sensing information enhancement and merging, the SENDIMAGE laboratory has developed applications in the fields of terrain modeling, heat island monitoring, ozone mapping, phenology monitoring, and so on. The understanding and recognition of typical geo-phenomena has been deepened by the use of data with high accuracy, resolution, and spatio-temporal continuity. These research results have been published in Remote Sensing of Environment, IJGIS, and other international journals.
- Long-term and Fine-scale Monitoring of the Urban Heat Island Effect
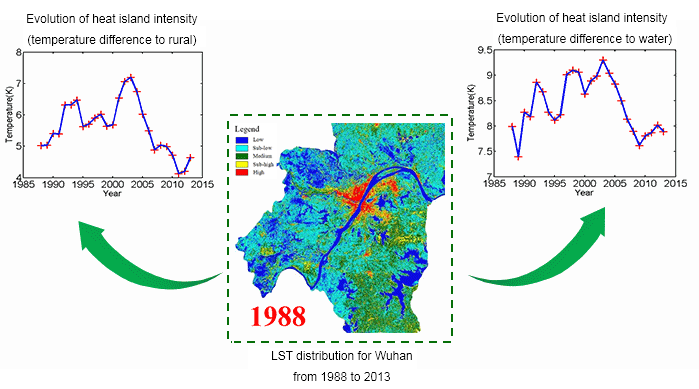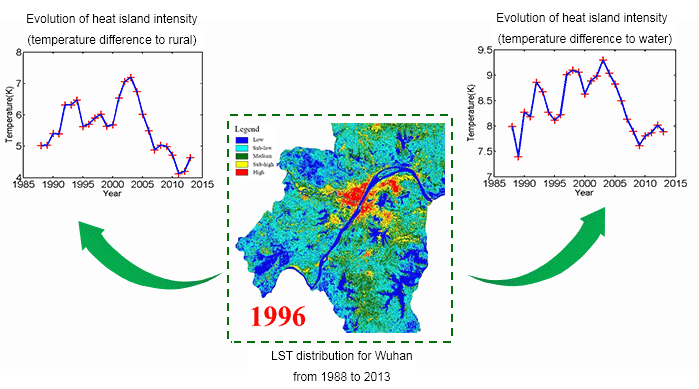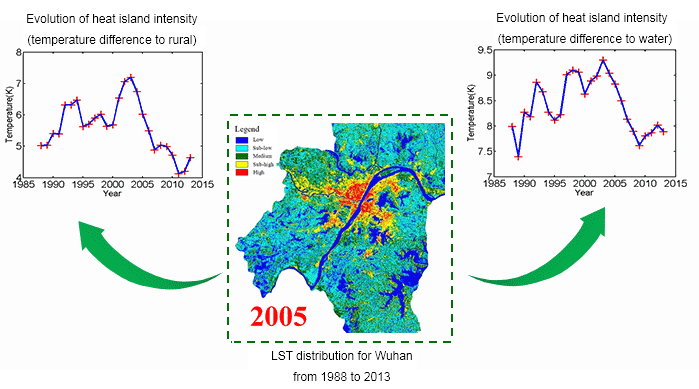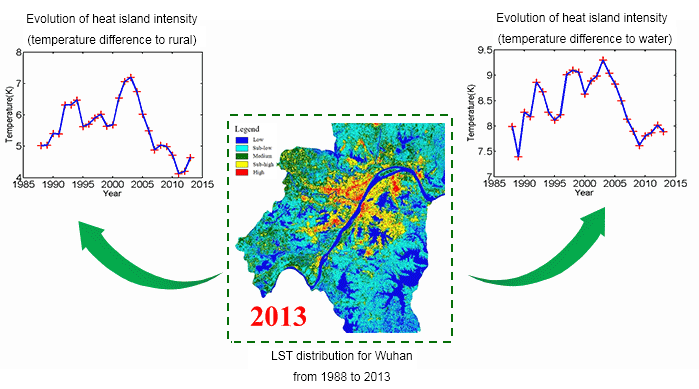
The trade-off between the temporal and spatial resolutions, and/or the influence of cloud cover, makes it difficult to obtain continuous fine-scale satellite data for surface urban heat island (SUHI) analysis. To relieve these difficulties, we employs multi-temporal and multi-sensor fusion methods for a long-term and fine-scale summer SUHI analysis of the city of Wuhan in China. By integrating several series of satellite images, we generated 26-year (1988 to 2013) high spatial resolution (Landsat-like) summer land surface temperature (LST) data. This series of data was then used for a qualitative and quantitative analysis of the SUHI patterns, evolution characteristics, and mechanisms.


- Spatially Continuous and Daily Ozone Mapping
The SENDIMAGE laboratory generated a spatio-temporal continuous ozone mapping product by the use of advanced reconstruction methods. The main work is to reconstruct the wide missing areas of information in the level 3 ozone product (OMTO3e) obtained from the Aura Ozone Monitoring Instrument.
These ozone products are shared on our website for free download.

- Digital Terrain Reconstruction and Analysis
The motivation behind the proposed multi-scale fusion algorithm is to obtain a seamless integration of data from multi-source digital elevation models (DEMs) with different resolutions and spatial extents, and thus to reconstruct the desired data with a high resolution and extensive coverage. We integrated resolution enhancement, noise suppression, and data void filling into a universal framework. The reconstructed data with an enhanced accuracy can be applied in various fields such as relief analysis and hydrological studies.

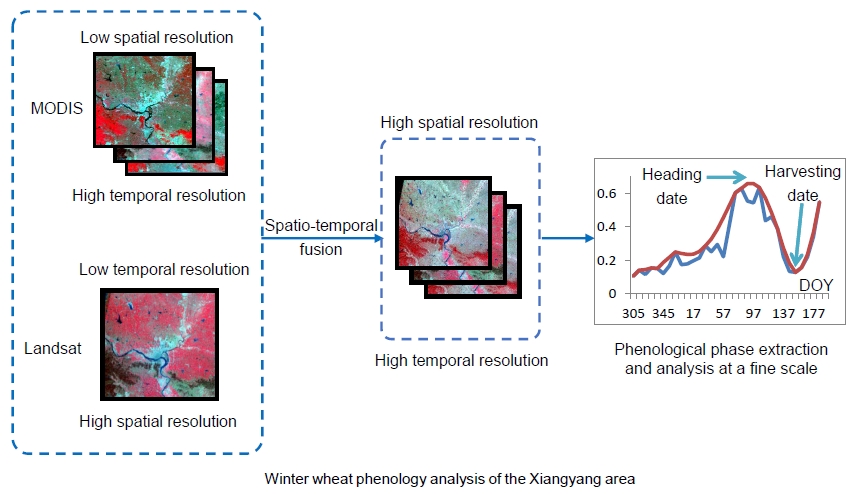
- Phenology Monitoring
Spatio-temporal fusion methods for multi-sensor data are used to obtain Landsat-like images with MODIS temporal resolution. These images can provide more detailed land-cover types and more reliable phenology information than either image source alone. We used fused datasets for the Xiangyang area for winter wheat crop mapping and phenological phase extraction and analysis, and we then noted some relationships between phenology and climate change. The results of this study are a useful reference for winter wheat planting in northern China.